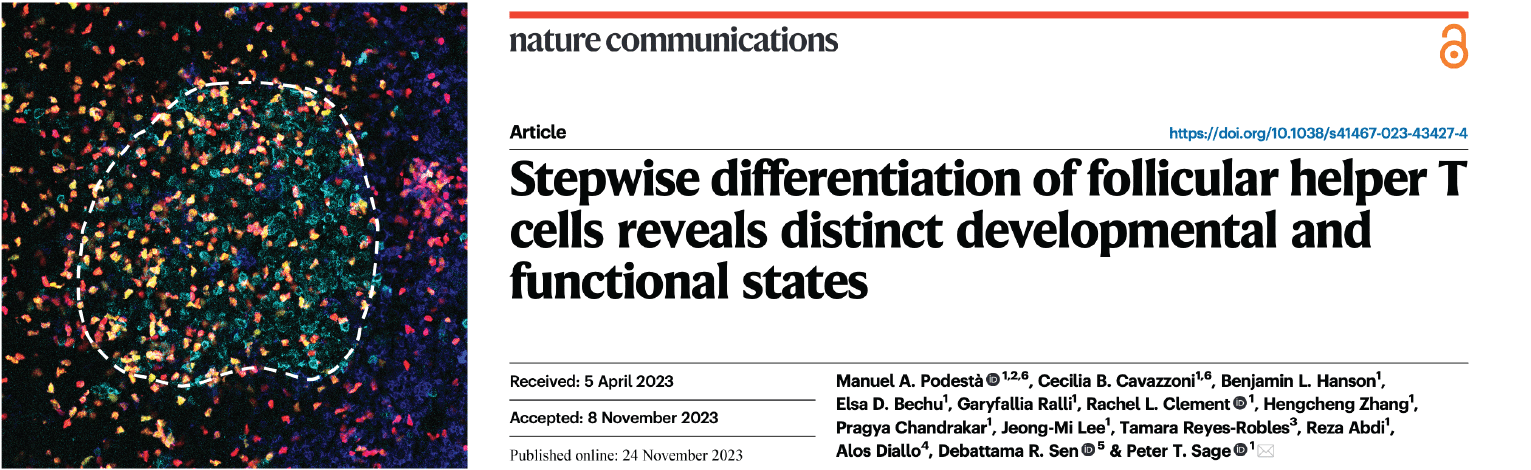


IL-21-producing effector Tfh cells promote B cell alloimmunity in lymph nodes and kidney allografts.
Transcriptionally Distinct B Cells Infiltrate Allografts After Kidney Transplantation
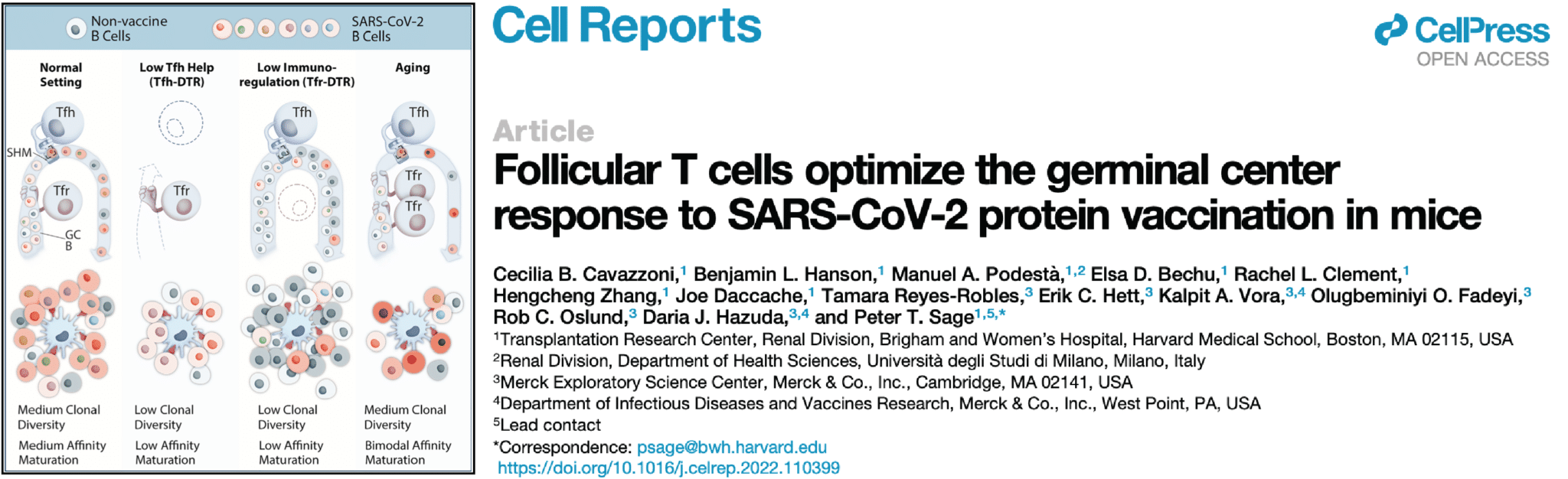
Follicular T cells Optimize the Germinal Center Response to SARS-CoV-2 Protein Vaccination in Mice
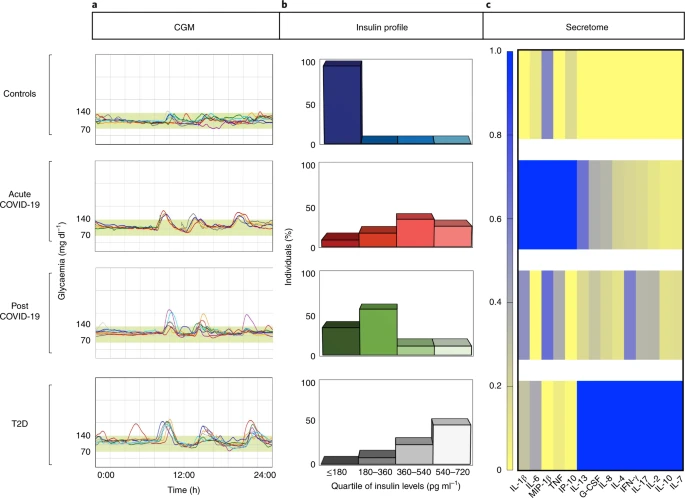
Acute and long-term disruption of glycometabolic control after SARS-CoV-2 infection
Patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) are reported to have a greater prevalence of hyperglycaemia. Cytokine release as a consequence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection may precipitate the onset of metabolic alterations by affecting glucose homeostasis. Here we describe abnormalities in glycometabolic control, insulin resistance and beta cell function in patients with COVID-19 without any pre-existing history or diagnosis of diabetes, and document glycaemic abnormalities in recovered patients 2 months after onset of disease. In a cohort of 551 patients hospitalized for COVID-19 in Italy, we found that 46% of patients were hyperglycaemic, whereas 27% were normoglycaemic. Using clinical assays and continuous glucose monitoring in a subset of patients, we detected altered glycometabolic control, with insulin resistance and an abnormal cytokine profile, even in normoglycaemic patients. Glycaemic abnormalities can be detected for at least 2 months in patients who recovered from COVID-19. Our data demonstrate that COVID-19 is associated with aberrant glycometabolic control, which can persist even after recovery, suggesting that further investigation of metabolic abnormalities in the context of long COVID is warranted.
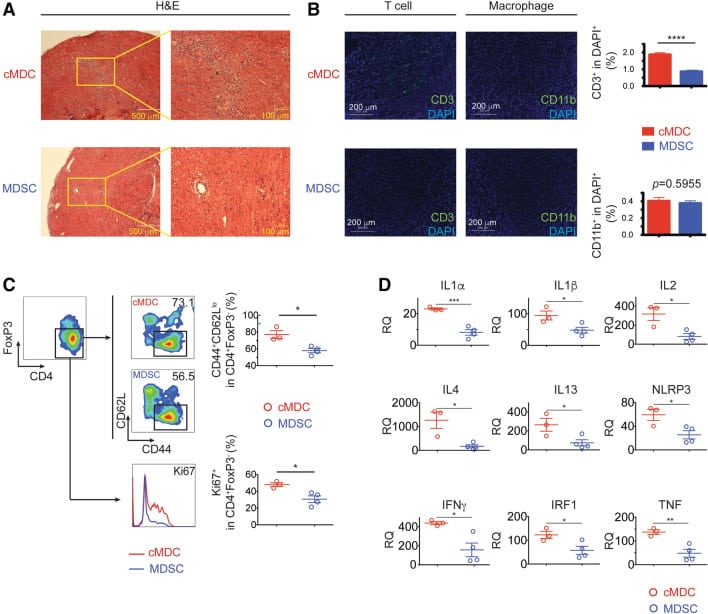
Donor myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) prolong allogeneic cardiac graft survival through programming of recipient myeloid cells in vivo
Solid organ transplantation is a lifesaving therapy for patients with end-organ disease. Current immunosuppression protocols are not designed to target antigen-specific alloimmunity and are uncapable of preventing chronic allograft injury.
Follicular T cells mediate donor-specific antibody and rejection after solid organ transplantation
Following solid organ transplantation, a substantial proportion of chronic allograft loss is attributed to the formation of donor-specific antibodies (DSAs) and antibody-mediated rejection (AbMR).
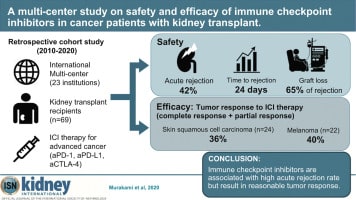
A multi-center study on safety and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with kidney transplant
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are widely used for various malignancies. However, their safety and efficacy in patients with a kidney transplant have not been defined. To delineate this, we conducted a multicenter retrospective study of 69 patients with a kidney transplant receiving ICIs between January 2010 and May 2020.
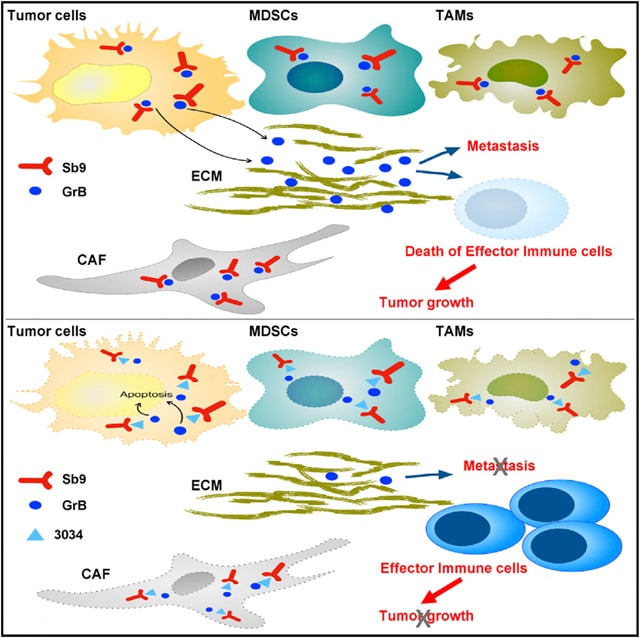
Direct Tumor Killing and Immunotherapy through Anti-SerpinB9 Therapy
Cancer therapies kill tumors either directly or indirectly by evoking immune responses and have been combined
with varying levels of success. Here, we describe a paradigmto control cancer growth that is based on
both direct tumor killing and the triggering of protective immunity.
Regulatory T cells engineered with TCR signaling–responsive IL-2 nanogels suppress alloimmunity in sites of antigen encounter
Adoptive cell transfer of ex vivo expanded regulatory T cells (Tregs) has shown immense potential in animal models of auto- and alloimmunity. However, the effective translation of such Treg therapies to the clinic has been slow.
